How Grid-Tied PV Works
The utility company installs a bi-directional meter that measures the electricity you both consume from the grid and export to the grid. This meter records the "net" difference between the electricity you consume and the electricity you export. At the end of a billing cycle (usually monthly), your utility company calculates your net energy usage. If you have exported more electricity than you have imported, you receive credits for the excess energy. These credits can offset the cost of electricity you consume from the grid during times when your solar panels aren't generating enough power, such as at night or during cloudy days. Depending on the net metering policy offered by your utility, unused credits may roll over to future months or expire at the end of the billing year.
In Island County (PSE) these expire on March 31 of every year.
In Island County (PSE) these expire on March 31 of every year.
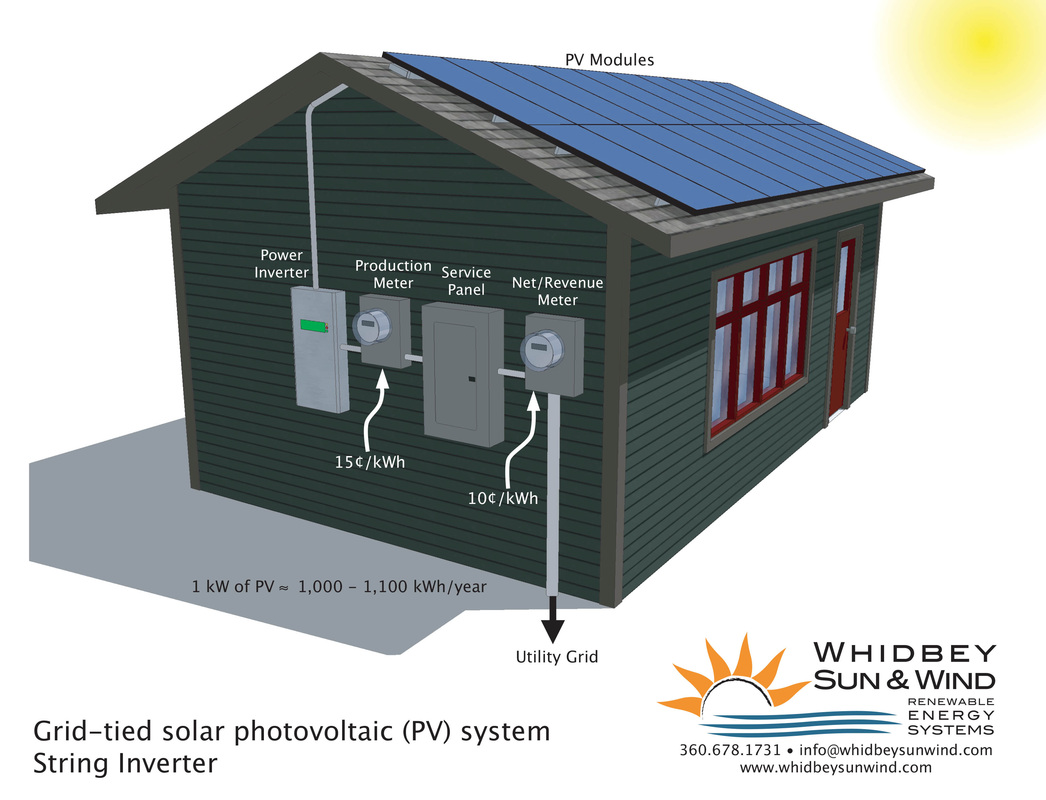
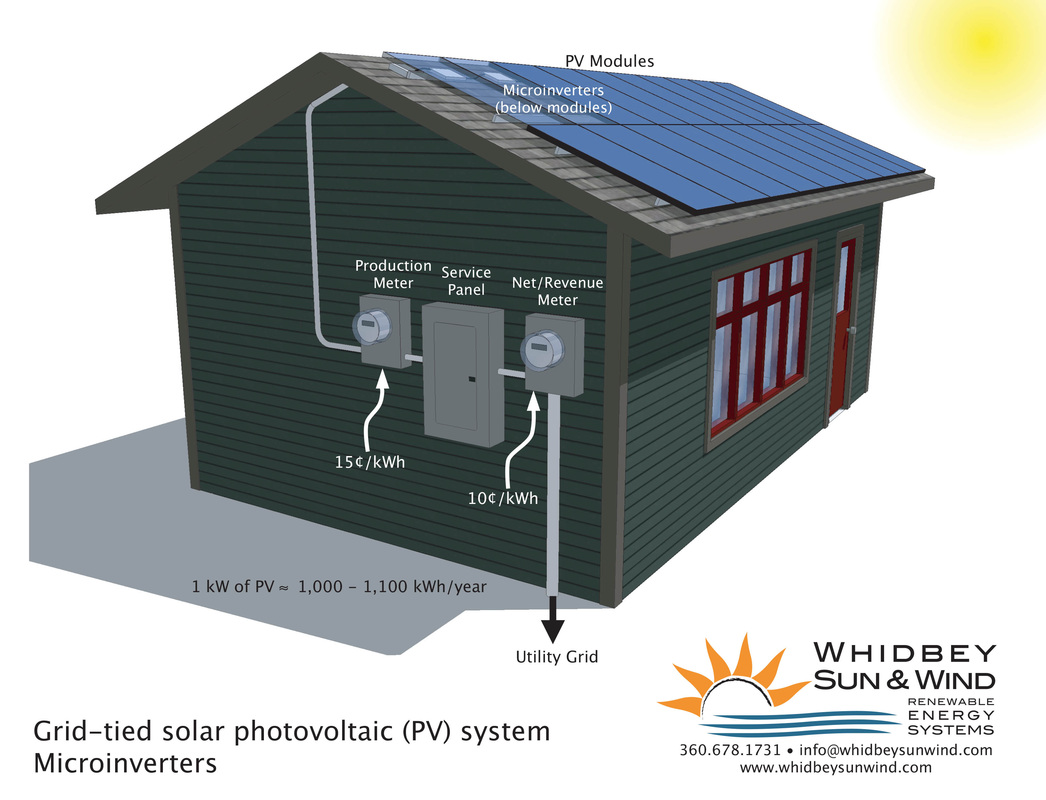
Batteryless grid-tie systems are the most popular type of PV grid-tie system; they are simple and efficient, providing power to residential and commercial spaces.
- In a batteryless PV grid-tie system, DC electricity is generated by PV modules.
- Next, the DC electricity is converted into usable AC power by an utility-interactive inverter.
- If a string inverter is used, many PV modules will be connected to one central inverter. String inverters, such as the Sunny Boy, may be wired to a single series string of 12-24 PV modules.
- If micro-inverters are used, then each PV module will interface with its own individual inverter device.
|
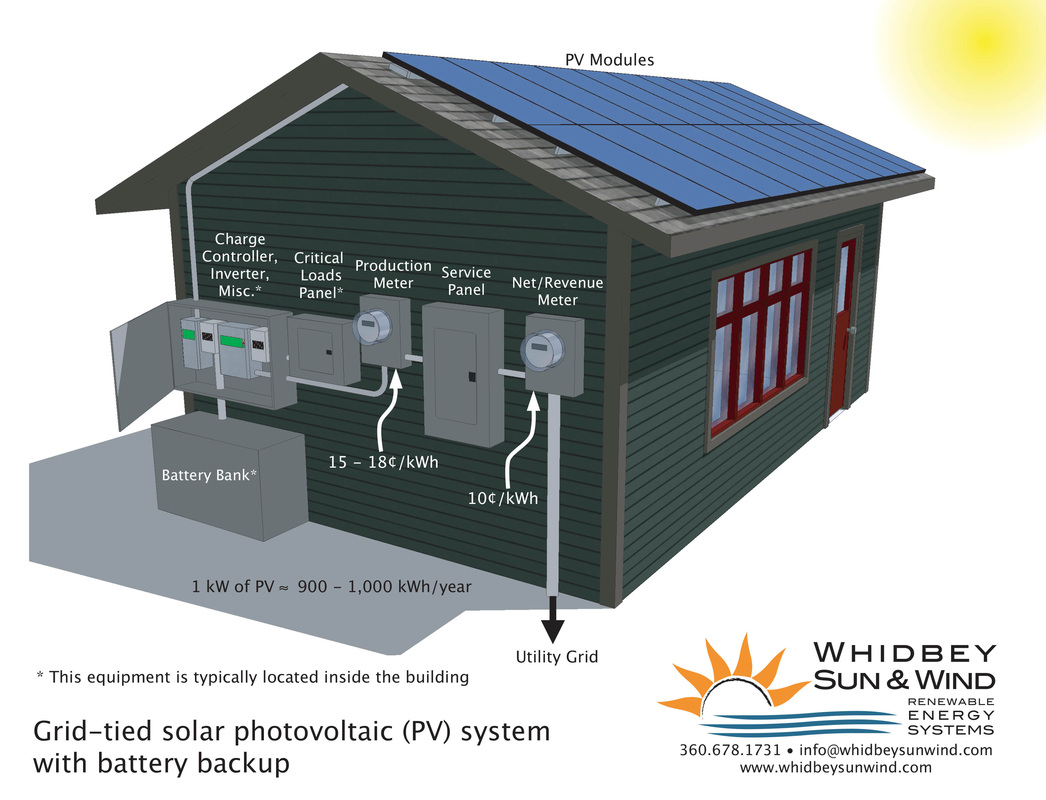
Battery-based grid tied systems employs batteries as a part of grid-tie system architecture to provide backup power in the event of an outage (UPS). Adding battery capacity will reduce overall system efficiency by 10%. They require periodic maintenance, which may be performed by an informed system user.
|